Berkani F, Dahmoune F, Kaadri N, Serralheiro ML, Ressaissi A, Abbou A, Kaci M, Meziane S, Achat S, Benzitoune N, Adouane M, Madani K, Mouni L .
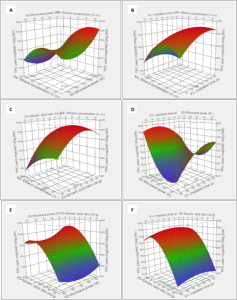
Jujube fruit is a considerable source of antioxidants that could be used as ingredients against several diseases. The optimization of microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) of bioactive compounds from Z. lotus pulp and peel (Zlp) was achieved using response surface methodology. The effect of the extraction parameters (microwave power “MW”, extraction time, ethanol/water solvent and liquid–solid ratio) on the total phenolic compounds (TPC) was well described by second-degree regression model. The liquid chromatography-high resolution tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS) was done. Best results were obtained at 600 W MW power, 180 s irradiation time, 51% ethanol concentration and 47:1 mL/g solvent-to solid ratio obtaining 7473.38 ± 740.55 mg GAE/100 g of TPC, 1019.96 ± 75.03 mg CE/100 g of TFC, 14,253.11 ± 2453.86 mg CE/100 g of TTC. LC–MS–MS determined that from all phytochemicals, 44.51% of the extract was flavonoids which represent 80.75% of all secondary metabolites from which 5-hydroxy-7-O-nerylflavanone is found to be the most abundant one. The extracts revealed the presence of 34 bioactive compounds, from which 10 phenolic compounds have never been previously identified from Zizyphus plant. The Zlp extract exhibited a greatest antioxidant effects by PAOT, DPPH, and FRAP activity; as well as, a lowest cytotoxic effects against both HepG2 and MCF-7 cells. In a concentration of 1 mg/mL, Zlp produced a strong AChE inhibition. This research revealed that MAE is more rapid and an effective method to extract TPC recovery which can be used in food matrixes and/or in nutraceutical formulations for its good biological effect.
Doi: 10.1007/s11694-022-01437-8
Berkani F, Dahmoune F, Kaadri N, Serralheiro ML, Ressaissi A, Abbou A, Kaci M, Meziane S, Achat S, Benzitoune N, Adouane M, Madani K, Mouni L (2022) LC–ESI–MS/MS analysis, biological effects of phenolic compounds extracted by microwave method from Algerian Zizyphus lotus fruits. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization, , . doi: 10.1007/s11694-022-01437-8